Transgenic Animals Definition Biology
Transgenesis is the process by which mixing up of genes takes place.
Transgenic animals definition biology. A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been altered by the transfer of a gene or genes from another species or breed. To determine an unknown genes function. Transgenic plants can be made by introducing foreign DNA into a variety of different tissues.
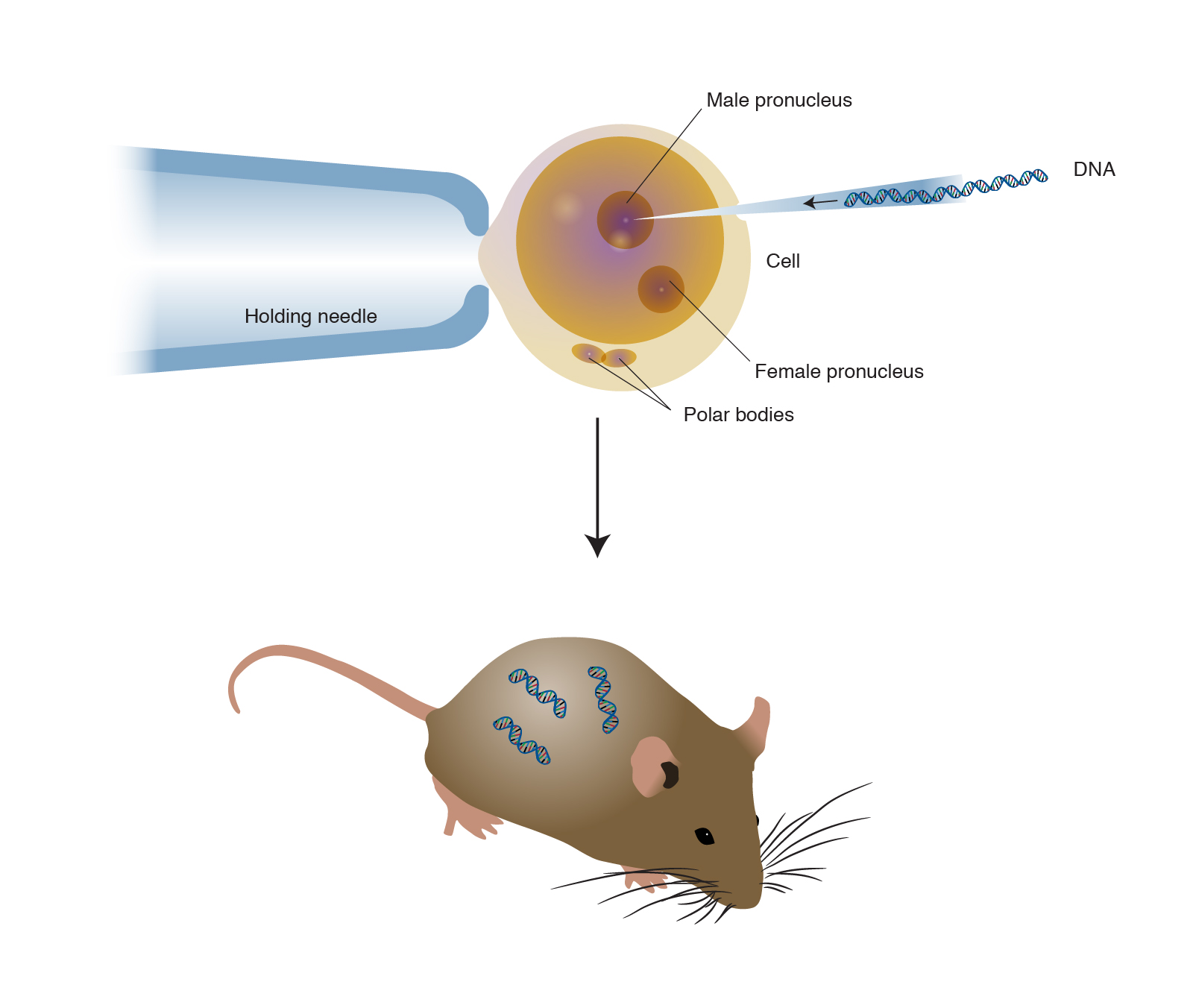
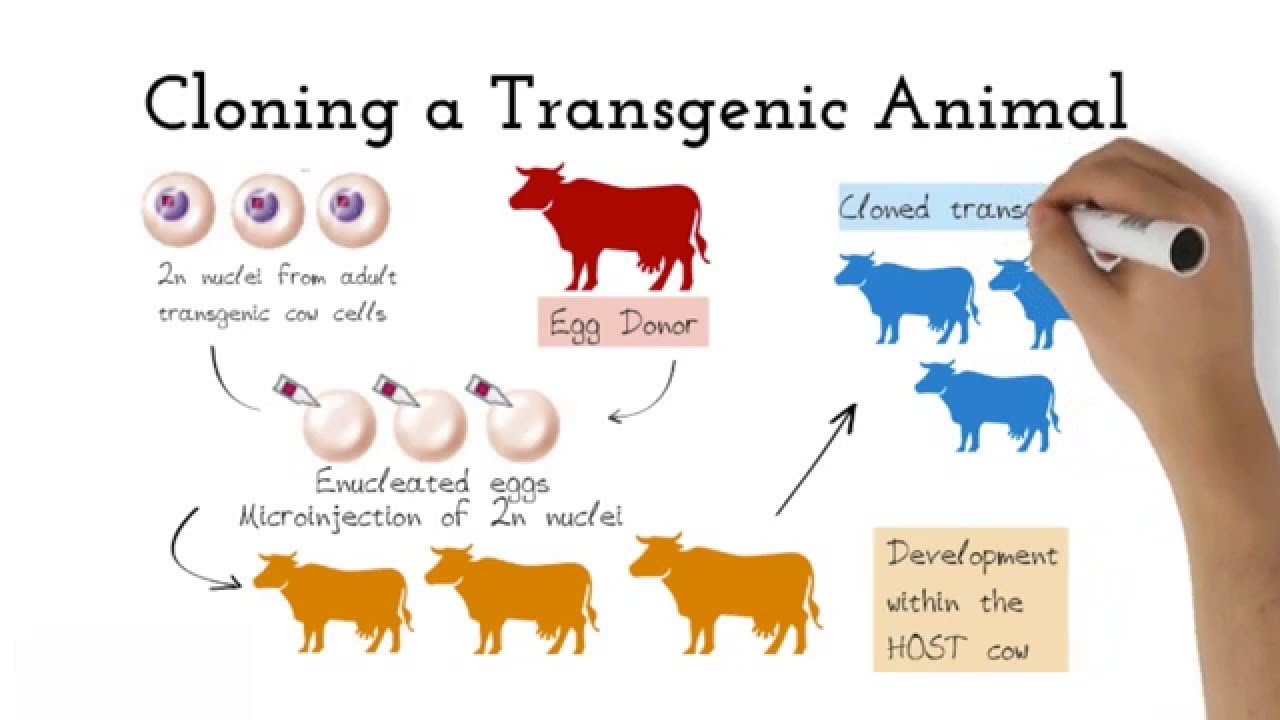
Transgenic means that one or more DNA sequences from another species have been introduced by artificial means. Arise from pluripotent stem cells. Transgenic animals are created by deliberately inserting a gene into the genome of an animal.
A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. Modified animals Animals Biology. Foreign genes are inserted into the germ line of the animal so it can be transmitted to the progeny.
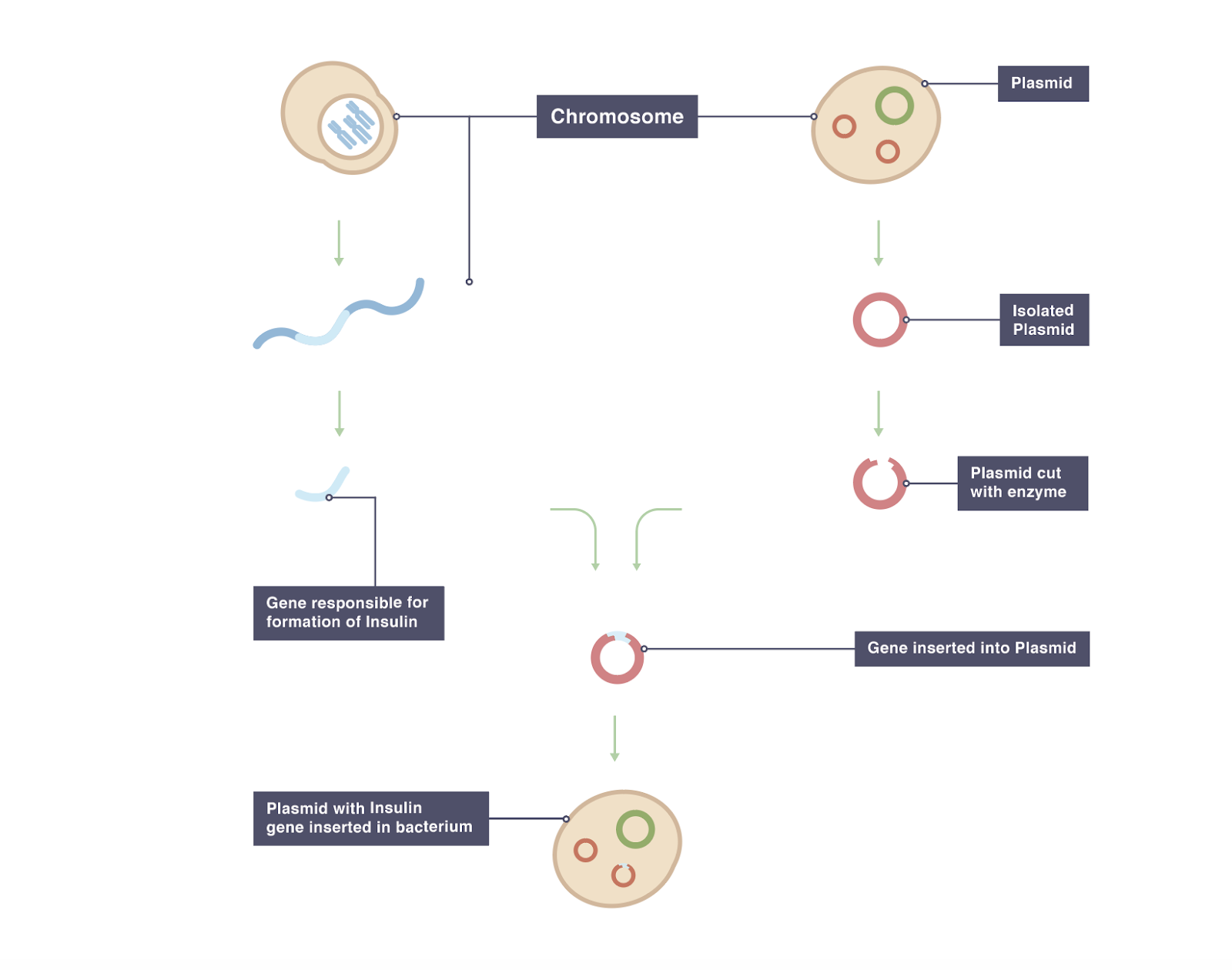
They are then exposed to the toxic substances and the effects studied. Recombinant DNA methodology is used to construct the gene that is intended to express desirable qualities during the growth and development of the recipient animal. BTransgenic animals are made that carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals.
For example we have transgenic models for diseases such. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology.
Animals usually are made transgenic by having a small sequence of foreign DNA injected into a fertilized egg or developing embryo. Animals transgenic animals or the offspring of such animals into which cloned genetic material has been experimentally transferred by microinjection of foreign dna either directly or into embryos or differentiated cell types. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome.

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)